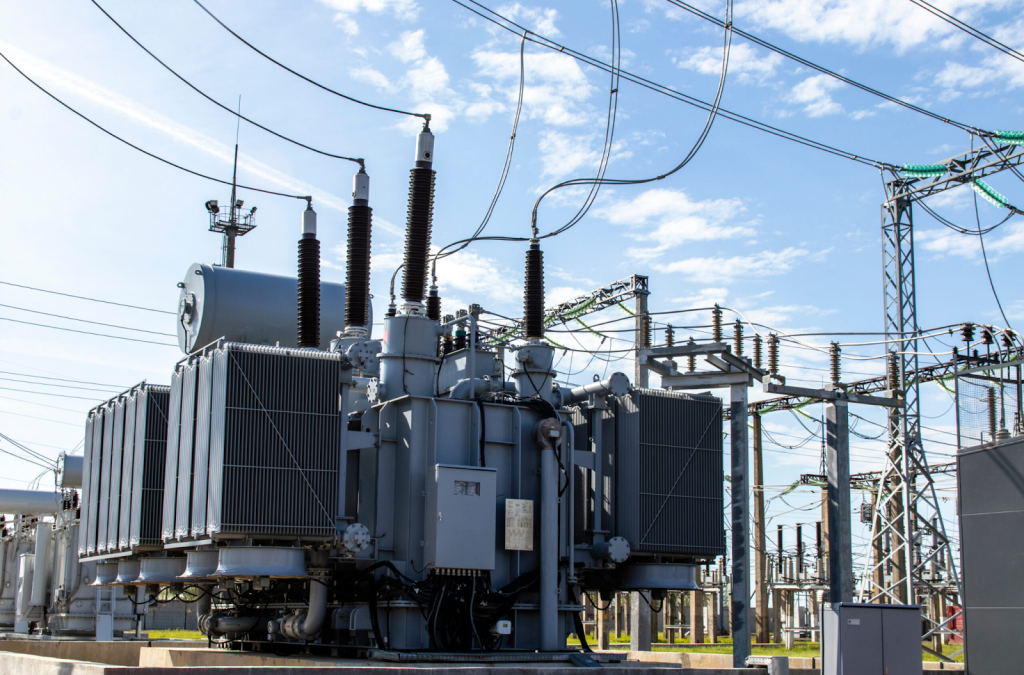
Electrical power transformers are critical components in the efficient distribution of electricity across power grids, ensuring that electrical energy reaches homes, industries, and businesses in a safe and effective manner. These devices play a key role in transforming voltage levels to ensure that the energy is transmitted without loss or safety concerns. This article explores the key features of electrical power transformers and how they benefit energy supply systems.
What is an Electrical Power Transformer?
An electrical power transformer is a static electrical device designed to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Its main function is to step up or step down voltage levels between the power generation source and the end consumer, thereby improving the efficiency and safety of electricity distribution.
Power transformers are typically used in electrical power stations, substations, and transmission lines. By altering voltage levels, they allow electricity to be transported over long distances at high voltage (for minimal energy loss) and then safely reduced to the correct voltage for consumption by homes and businesses.
Key Features of Electrical Power Transformers
- Voltage Regulation
Electrical power transformers are equipped to regulate voltage levels by either increasing (step-up transformers) or decreasing (step-down transformers) the voltage. This regulation ensures that the power remains stable during transmission, thus preventing fluctuations that could damage electrical devices. - Capacity and Rating
Power transformers come in a range of sizes, from small units designed for residential or small-scale industrial use to massive transformers capable of handling large amounts of electricity. Each transformer has a specific capacity, usually measured in kilovolt-amperes (kVA) or megavolt-amperes (MVA), that determines the amount of power it can handle. - Insulation and Safety
An essential feature of any electrical power transformer is its insulation system. It is crucial for preventing electrical faults, such as short circuits or arcing. Insulation materials, such as oil or gas, are used to cool the transformer and improve its electrical resistance, ensuring it can function efficiently and safely. - Efficiency and Losses
Electrical power transformers are designed to minimize losses during energy transfer. However, some energy is inevitably lost in the form of heat, typically due to resistance in the coils and magnetic losses in the core. Higher efficiency transformers are engineered to reduce these losses, ensuring maximum energy transfer with minimal waste. - Design and Construction
The construction of power transformers involves various components, including the core, windings, tap changer, and bushings. The core is usually made of laminated steel to minimize energy losses, while the windings are typically copper or aluminum, chosen for their excellent conductivity.
How Electrical Power Transformers Benefit Your Energy Supply
- Efficient Energy Distribution
Power transformers significantly enhance the efficiency of electrical energy distribution. By stepping up the voltage for transmission over long distances, transformers minimize energy losses, ensuring that electricity reaches its destination with minimal wastage. - Improved Safety
Voltage regulation by electrical power transformers reduces the risks of over-voltage, which could lead to equipment damage, fires, or even electrical hazards. By maintaining optimal voltage levels, transformers ensure a safer energy supply for both residential and industrial consumers. - Cost-Effectiveness
Without transformers, electricity would need to be transmitted at lower voltages, which would require larger and more expensive conductors to transmit the same amount of power. By using electrical power transformers to step up the voltage and reduce losses, the overall cost of energy transmission is lower, making electricity more affordable for consumers. - Flexibility in Energy Supply
Transformers also provide flexibility in the energy supply by allowing energy to be routed to different areas depending on demand. By adjusting the voltage levels, electrical power transformers ensure that power can be allocated where it is needed most, helping to avoid blackouts or under-supply in critical areas. - Supporting Renewable Energy Integration
As renewable energy sources like solar and wind power become more common, electrical power transformers play an essential role in integrating these variable power sources into the grid. Transformers can step up or down the voltage from renewable energy plants, allowing them to be efficiently connected to the broader power network.
Conclusion
Electrical power transformers are indispensable to modern electrical grids, offering a safe, efficient, and cost-effective means of transmitting and distributing electrical energy. Their key features—such as voltage regulation, high capacity, and safety mechanisms—ensure that power is delivered reliably and efficiently to homes and businesses. The continued evolution of transformer technology supports a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure, enabling the smooth integration of renewable energy sources and helping to meet growing global electricity demand.